The IEEE 802.3 SNAP
Frame Format
Introduction
While the
original 802.3
specification worked well, the IEEE realized that some
upper layer protocols required an Ethertype to work
properly. For example, TCP/IP uses the Ethertype to
differentiate between ARP packets and normal IP data
frames. In order to provide this backwards compatibility
with the Version II frame type, the 802.3
SNAP (SubNetwork
Access
Protocol) format was
created.
The
SNAP Frame Format consists
of a normal 802.3 Data Link Header followed by a normal
802.2 LLC Header and then a 5 byte
SNAP field, followed by the normal user data and
FCS.
You can see
the above mentioned headers in the
3D diagram of the frame below:
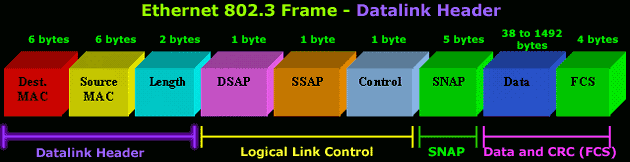
THE DATA LINK HEADER
Offset 0-5: The Destination Address
- The
first six bytes of an Ethernet frame make up the
Destination Address. The Destination Address
specifies to which adapter the data frame is being
sent. A Destination Address of all ones specifies a
Broadcast Message that is read in by all receiving
Ethernet adapters.
- The
first three bytes of the Destination Address are
assigned by the IEEE to the vendor of the adapter
and are specific to the vendor.
- The
Destination Address format is identical in all
implementations of Ethernet.
Offset 6-11: The Source Address
- The
next six bytes of an Ethernet frame make up the
Source Address. The Source Address specifies from
which adapter the message originated. Like the
Destination Address, the first three bytes specify
the vendor of the card.
- The
Source Address format is identical in all
implementations of Ethernet.
Offset 12-13: Length
- Bytes
13 and 14 of an Ethernet frame contain the length of
the data in the frame, not including the preamble,
32 bit CRC, DLC addresses, or the Length field
itself. An Ethernet frame can be no shorter than 64
bytes total length and no longer than 1518 bytes
total length.
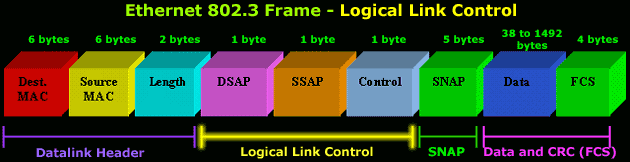
THE 802.2 LOGICAL LINK CONTROL (LLC) HEADER
Following the Data Link Header is the Logical Link
Control Header, which is described in the IEEE 802.2
Specification. The purpose of the LLC header is to
provide a "hole in the ceiling" of the Data Link Layer.
By specifying into which memory buffer the adapter
places the data frame, the LLC header allows the upper
layers to know where to find the data.
Offset 15: The DSAP
- The
DSAP, or Destination Service Access Point, is a 1
byte field that simply acts as a pointer to a memory
buffer in the receiving station. It tells the
receiving NIC in which buffer to put this
information. This functionality is crucial in
situations where users are running multiple protocol
stacks, etc...
Offset 16: The SSAP
- The
SSAP, or Source Service Access Point is analogous to
the DSAP and specifies the Source of the sending
process.
- In
order to specify that this is a SNAP frame, the SSAP
is set to AA hex.
Offset 17: The Control Byte
-
Following the SAPs is a one byte control field that
specifies the type of LLC frame that this is.
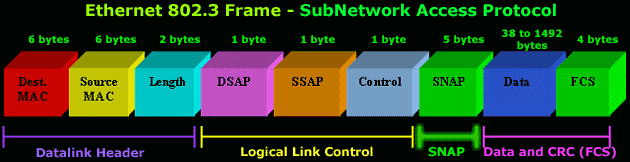
THE SUB-NETWORK ACCESS PROTOCOL (SNAP) HEADER
Offset 18-20: The Vendor Code
- The
first 3 bytes of the SNAP header is the vendor code,
generally the same as the first three bytes of the
source address although it is sometimes set to zero.
Offset 21-22: The Local Code
-
Following the Vendor Code is a 2 byte field that
typically contains an Ethertype for the frame. This
is where the backwards compatibility with Version II
Ethernet is implemented.
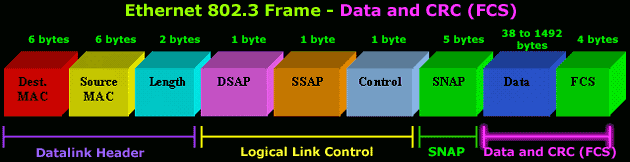
USER DATA AND THE FRAME CHECK SEQUENCE (FCS)
Data: 38-1492 Bytes
-
Following the 802.2 header are 38 to 1,492 bytes of
data, generally consisting of upper layer headers
such as TCP/IP or IPX and then the actual user data.
FCS: Last 4 Bytes
- The
last 4 bytes that the adapter reads in are the Frame
Check Sequence or CRC. When the voltage on the wire
returns to zero, the adapter checks the last 4 bytes
it received against a checksum that it generates via
a complex polynomial. If the calculated checksum
does not match the checksum on the frame, the frame
is discarded and never reaches the memory buffers in
the station.
|
