Media Access
Control - MAC Addresses
Introduction
Media Access Control
(MAC)
addresses
are talked about in
various sections on the site, such as the OSI-Layer
2, Multicast, Broadcast and Unicast. We are
going to analyse them in depth here so we can
get a firm understanding of them since they are
part of the fundamentals of networking.
MAC addresses
are physical addresses, unlike IP addresses
which are logical addresses. Logical addresses
require you to load special drivers and
protocols in order to be able to configure your
network card/computer with an IP Address,
whereas a MAC address doesn't require any
drivers whatsoever. The reason for this is that
the MAC address
is actually "burnt-in" into your network card's
memory chipset.
The Reason for MAC
Each computer on a network needs to be
identified in some way. If you're thinking of IP
addresses, then you're correct to some extent,
because an IP address does identify one unique
machine on a network, but that is not enough.
Got you mixed up?
Check the diagram and explanation below to see
why :

You see, the IP address of
a machine exists on the
3rd Layer
of the OSI model and, when
a packet reaches the computer, it will travel
from Layer 1
upwards, so we need to be
able to identify the computer before
Layer 3.
This is where the
MAC address -
Layer 2
comes into the picture. All machines on a
network will listen for packets that have their
MAC address in the destination field of the
packet (they also listen for broadcasts and
other stuff, but that's analysed in other
sections). The
Physical Layer
understands the electrical signals on the
network and creates the frame which gets passed
to the Datalink
layer. If the
packet is destined for the computer then the
MAC address
in the destination field of the packet will
match, so it will accept it and pass it onto the
Layer above
(3)
which, in turn, will check
the network address of the packet (IP Address),
to make sure it matches with the network address
to which the computer has been configured.
Looking at a MAC
Let's now have a look at a
MAC address
and see what it looks
like! I have taken my workstations MAC address
as an example:

When looking at a MAC address, you will always
see it in HEX format. It is very rare that a MAC
address is represented in Binary format because
it is simply tooooo long as we will see futher
on.
When a vendor, e.g Intel,
creates network cards, they don't just give them
any MAC address
they like, this would
create a big confusion in identifying who
created this network card and could possibly
result in clashing with another MAC address from
another vendor e.g D-link, who happened to
choose the same MAC address for one of their
network cards !
To make sure problems like
this are not experienced, the IEEE group split
the MAC address
in half, and used the
first half
to identify the vendor,
and the second half
is for the vendor to
allocate as serial numbers:
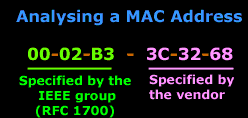
The
Vendor code
is specified by RFC -
1700. You might find a particular vendor having
more than just one code; this is because of the
wide range of products they might have. They
just apply for more, as they need !
Keep in mind that even tho
the MAC address
is "burnt-in" to the network card's memory, some
vendors will allow you to download special
programs to change the
second half
of the
MAC address
on the card. This is
because the vendors actually reuse the same MAC
addresses for their network cards because they
create so many that they run out of numbers !
But at the same time, the chances of you buying
two network cards which have the same MAC
address are so small that it's almost impossible
!
Let's start talking bits and bytes!
Now that we know what a
MAC address looks like, we need to start
analysing it. A MAC address of any network card
is always the same length, that is,
6 Bytes
long or
48 Bits
long. If you're scratching your head wondering
where these figures came from, then just have a
look at the picture below which makes it a bit
easier to understand:
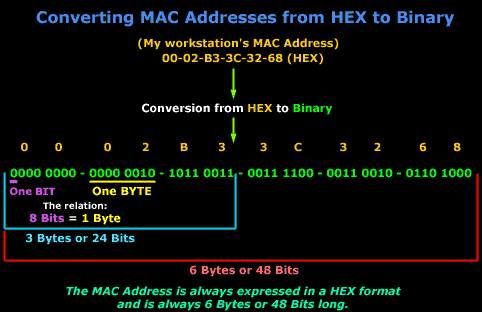
So that completes the
discussion regarding
MAC Addresses!
I hope you have understood it all because it's
very important so you can expand your knowledge
and truly understand what happens in a network !
