Cisco Basics - User
Exec Mode
Introduction
Let's see what
it looks like to be in each one of these modes. Here I
have telneted into our lab router and I am in
User Exec Mode:
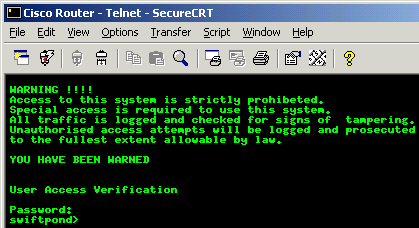
The easiest
way to keep track of the mode you're in is by looking at
the prompt. The ">" means we are in
User Exec Mode. From this
mode, we are able to get information like the version of
IOS, contents of the
Flash memory and a few
others.
Now, let's
check out the available commands in this mode. This is
done by using the "?" command and hitting enter:
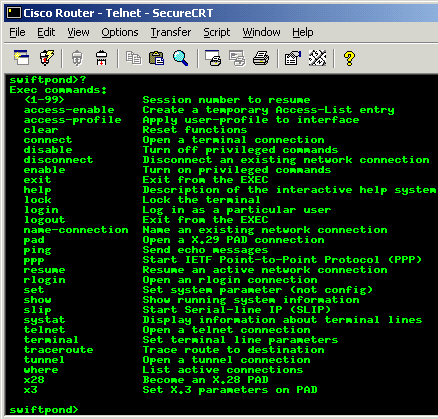
Wow, see
all those commands available ? And just to think that
this is considered a small portion of the total commands
available when in Privileged Mode
! Keep in mind that when you're in the console and
configuring your router, you can use some short cuts to
save you typing full command lines. Some of these are :
Tab: By typing the first
few letters of a command and then hitting the
TAB key, it will
automatically complete the rest of the command. Where
there is more than one command starting with the same
characters, when you hit TAB
all those commands will be displayed. In the picture
above, if i were to type "lo"
and hit TAB, I would get a
listing of "lock,
login and
logout" because all 3
commands start with "lo".
?: The question mark symbol
"?" forces the router to
print a list of all available commands. A lot of the
commands have various parameters or interfaces which you
can combine. In this case, by typing the main command
e.g "show" and then putting
the "?" you will get a list
of the subcommands. This picture shows this clearly:
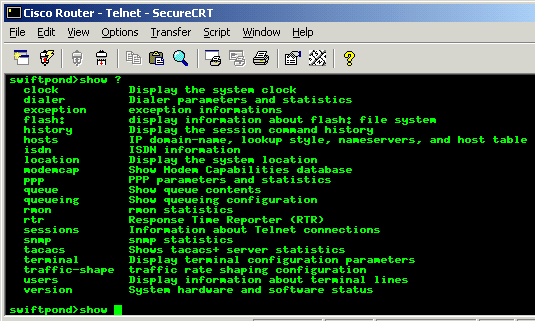
Other
shortcut keys are :
CTRL-A: Positions the
cursor at the beginning of the line.
CTRL-E: Positions the
cursor at the end of the line.
CTRL-D: Deletes a
character.
CTRL-W: Deletes a whole
word.
CTRL-B: Moves cursor back
by one step.
CTRL-F: Moves cursor
forward by one step.
One of the
most used commands in this mode is the "Show"
command. This will allow you to gather a lot of
information about the router. Here I have executed the "Show
version" command, which displays various
information about the router:
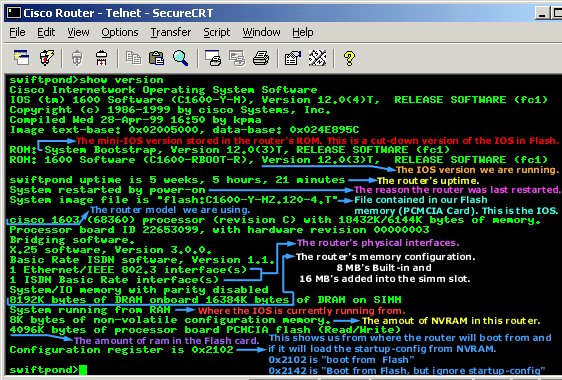
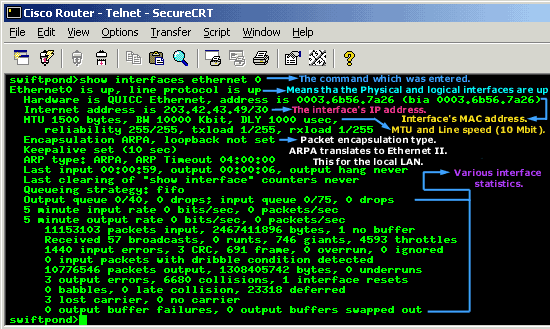
The "Show
Interface <interface>
" command shows us information on a particular
interface. This includes the IP address, encapsulation
type, speed, status of the physical and logical aspect
of the interface and various statistics. When issuing
the command, you need to replace the <interface>
with the actual interface you want to look at. For
example, ethernet 0,
which indicates the first ethernet interface :
Some other
generic commands you can use are the show
"running-config" and show "startup-config".
These commands show you the configuration of your
router.
The
running-config refers to
the running configuration, which is basically the
configuration of the router loaded into its memory at
that time.
Startup-config refers to
the configuration file stored in the NVRAM. This, upon
bootup of the router, gets loaded into the router's RAM
and then becomes the running-config
!
So you can
see that User Exec Mode is
used mostly to view information on the router, rather
than configuring anything. Just keep in mind that we are
touching the surface here and not getting into any
details.
This
completes the User Exec Mode
section. If you like, you can go back and continue to
the Privileged Mode
section. |
